East Sussex Healthcare NHS Trust
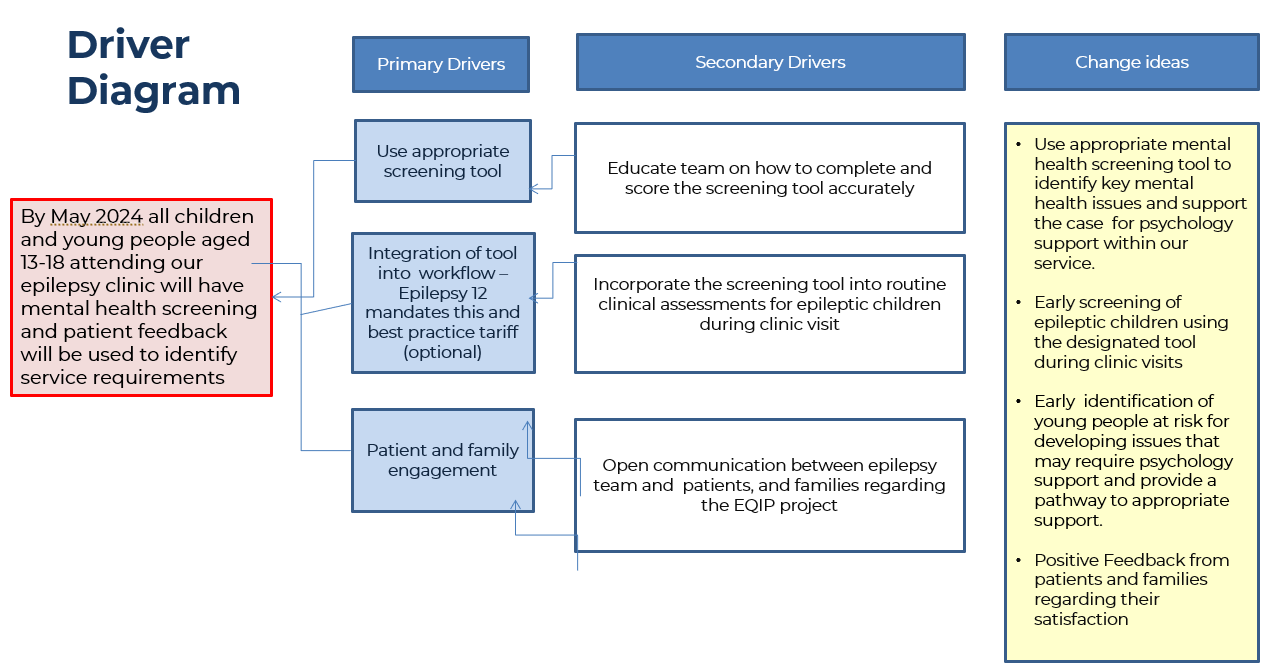
By May 2024 all children / young people aged 13 – 18 attending our epilepsy clinic will have mental health screening, use patient feedback to identify service requirements

Project aim
By May 2024 all children / young people aged 13 – 18 attending our epilepsy clinic will have mental health screening, use patient feedback to identify service requirements.
Background
The East Sussex Healthcare NHS Trust provides acute paediatric care services at Conquest Hospital and Eastbourne District General Hospital. The team provides care for around 400 children and young people diagnosed with epilepsy, of whom over 30% have comorbidities such as ASD, ADHD, other neurodisabilities, and genetic conditions. Nearly 50% experience sleep regulation difficulties and behavioural conditions.
Project planning
In accordance with NICE standards of practice and epilepsy 12, all children should be screened for mental health issues
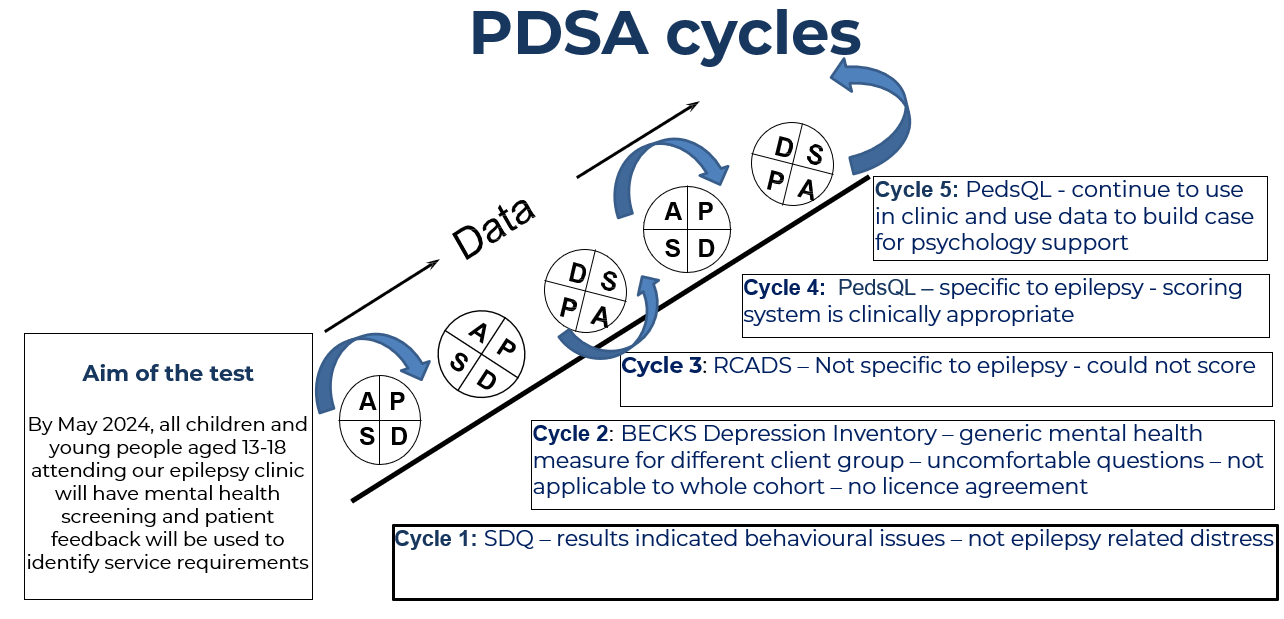
We had used Becks depression inventory and Strengths and difficulties questionnaires to screen mental health during epilepsy clinic consultations – this raised an ethical question since we had no pathway to any form of support/psychology services.
Patients previously had scores suggestive of Mild to Moderate Depression however they did not always meet the criteria for CAMHS intervention. Hence they were left untreated, and we had no way to identity what form of intervention was needed.
We initially trailed the Revised Children’s Anxiety and Depression RCADS Questionnaire – We could not find a successful way to score this tool.
We identified the PedsQL epilepsy module – Paediatric Quality of Life Inventory – Epilepsy specific measure of Quality of Life
Which is applicable to all age groups.
We explained the aim of our project – sought verbal consent
We asked our patients and their parents / carers attending clinic age 13 – 18 to complete the PedsQL tool
20 patients and parents/carers completed the tool
Tests, changes and what was learned in the process
PedsQL epilepsy module
Divided into 5 subsections:
- Cognitive function
- Executive Function
- Fatigue
- Mood and behaviour
- Impact
Existing versions:, for Toddlers (2-4 years of age), Young Children (5-7 years of age), Children (8-12 years of age), Teens (13-18 years of age), Young Adults (18-25 years of age)
- Parent and Young person segments
Scoring system via database
Colour on database changes to indicate severity (higher scores indicate higher health related quality of life).
If the total score is below a certain level then this will flag it up in red – indicating a lower quality of life and that further discussions about support might be helpful.
 |
 |
Results
After testing several tools, including the SDQ, RCADS, and Beck questionnaire, the team identified the PedsQL as the most suitable for their epilepsy patients, as it covers the impact on more areas of daily life.
Using the PedsQL epilepsy module screening tool the scoring is divided into five sections:
- Cognitive function
- Executive Function
- Fatigue
- Mood and behaviour
- Impact
Results are stored in a database, with different colours indicating the severity of the identified mental health condition (e.g., higher scores indicate a higher health-related quality of life). If the total scores fall below a certain threshold, they are flagged in red, indicating a lower quality of life and suggesting that further discussions about support might be beneficial.
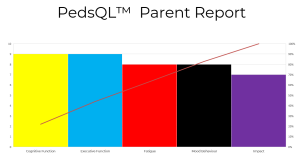
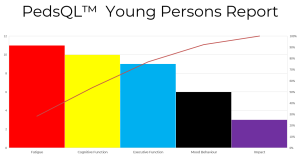
Results from children, young people and families that the team scored using the PedsQL screening tool uncovered that cognitive function was identified as one of the main problems by parents and young people. Impact was identified as the least important problem by children, young people and parents/carers. Fatigue and mood behaviour were also identified as being an issue.
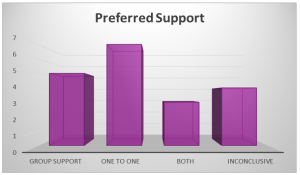
- Cognitive function were identified as main problems by Parents and Young people.
- Impact was identified as the least problem by both Young person and Parent.
- Fatigue and Mood behaviour were also identified as being an issue.
Patients completing Peds QL attending epilepsy clinic age 13 – 18 were asked to complete feedback questionnaire.
- The screening tools that we were previously using were not clinically effective – we had to find a tool that was more appropriate for our patients.
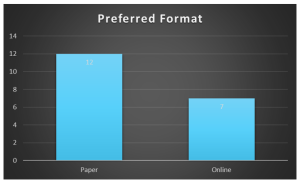
- The majority of patients liked using the PedsQL and completing the form on paper
- This is more convenient for us to use during consultation.
- The assumption was that mood would be the main problem.
- The sample size is small – we plan to continue using Peds QL to involve all our cohort – divide into 2 cohorts eg epilepsy and neurodiversity and epilepsy only.
- We abandoned Becks, SDQ and RCADS – we plan to continue using PedsQL and gather more data.
- We will continue to gather feedback from our patients and their carer’s
 |
 |
 |
 |
Challenges
- No dedicated time for Project
- Small team – big caseload.
Key issues that emerged
- Clinical cut off not yet identified for scoring Peds QL
- Best practice tariff component for psychology is small – is not enough incentive
- What would you have done differently?
We could use the PedsQL on wider population including younger age group for early identification/ intervention
Successes
- We are now using PedsQL
- We will start to use the tool on all age groups with the aim of early identification of problems.
- Continue to gather data and use this as a case to direct service requirement.
- Planning ongoing meetings with Psychologist working in our trust for case consultation if patients have identified a specific issues.
- Peds QL was clinically useful.
- Using Peds QL prior to clinic appointment can help direct questions during consultation.
Lessons learned
- We have a dedicated Team
- We learnt how to get support from other services
- The Impact of epilepsy – wider picture
- Various tools that can be used
- Changes don’t happen overnight – dedication and commitment is needed over time
What did the EQIP teach you that you will use tin the future?
- How to implement changes
- How to develop and implement an idea using the available resources
- How to engage patients and their families
How have you changed as a team?
- Satisfaction that we have made a positive change
Big goals can be achieved through small steps!
Next steps
- Approach managers to build a business case for psychology support for epilepsy service.
- Psychologist to join epilepsy meetings for case consultation – for signposting to other services or other specific suggestions.
- Develop a resource pack of services and signposting to support.
- Present EQIP findings to audit and governance meeting locally.
- Submission of poster presentation to Epilepsy 12 Open UK conference.
East Sussex Healthcare NHS Trust EQIP team project presentation and poster
Download to view East Sussex Healthcare NHS Trust project presentation and poster
Team project presentation (1.3MB) Team project poster (906.6KB)